Role of Generative AI in IOT security

Generative AI can enhance IoT security by identifying suspicious activities and potential threats. It can Detect unusual behavior in IoT networks or devices and raise alerts. Analyze patterns to identify security vulnerabilities in real-time.
NOTE :- First understand the terms before going to introduction of Generative AI.
What is AI?
AI is the theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence.
What is Machine learning?
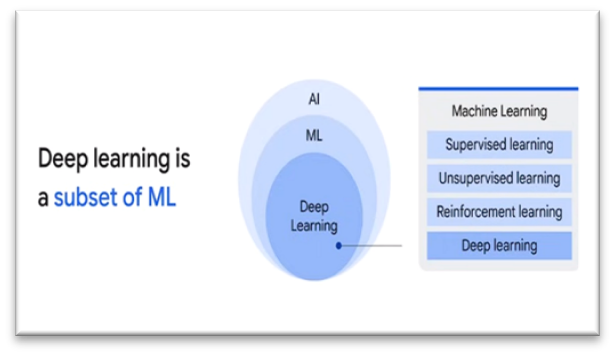
Machine learning is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling computers to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
It involves algorithms and statistical models that allow systems to automatically learn and make predictions or decisions based on data patterns.
There are four types of machine learning algorithms:
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
- Semi-supervised
- Reinforcement
What is Deep learning?
- Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers to learn and extract patterns from data.
- It’s capable of processing vast amounts of complex information to make predictions, recognize patterns, and perform tasks without explicit programming instructions.
a. Introduction of generative AI :-

- Generative AI is a type of Artificial Intelligence that creates new content based on what is has learned from existing content.
- The process of learning from existing content is called training and results in the creation of a statistical model.
- When given a prompt, generative AI uses this statistical model to predict what an expected response might be-and this generates new content.
b. Different types of cyber attacks :-

cyber attacks :- An attempt by hackers to damage or destroy a computer network or system.
- cyber attacks are generally classified into two types. They are
- Web-based attack
- System based attack
- Web-based attacks :-
- Injection attacks
- DNS spoofing
- Session hijacking attacks
- Phishing
- Brute force
- Denial of service
- Dictionary attacks
- URL interpretation
- File inclusion
- Man in the middle attack
- Injection attacks :- Injection attacks are a common cyberattack where an attacker injects malicious code into your web application to access your personal information or compromise your system.
- DNS spoofing :- It is a type of computer hacking, where by a data is introduced into a DNS resolvers cache causing diverting traffic to the attack computer or another computer. The DNS spoofing attacks can go on longer period of time without and being detected and can cause.
- Session hijacking attacks :- It is a security attack on a user session over a protected network. Web application create cookies to store the state and user session. By stealing the cookies, an attacker can have access to all of the users data.
- Phishing :- It is a attack which attempts to steal sensitive information like user login credential and credit number. It occurs when an attacker is masquerading as a trustworthy entity.
- Brute force :- It is an attacks which uses a trial and error method. It generates large number of guesses and validates them to passwords and pin. It is used by criminals to cracks encrypted data.
- Denial of service :- A denial of service (DoS) attack is an attack in which requests flood a server to the point that it can no longer cope with the load and crashes.
- Dictionary attacks :- Dictionary attacks are a type of cyber attack where an attacker tries to gain unauthorized access to a system or account by systematically entering a large number of words or phrases from a pre-built list, called a dictionary. This method involves trying every entry in the dictionary as a possible password or key, aiming to guess the correct one.
- URL interpretation : – URL interpretation attacks, also known as “URL parsing attacks” or “URL-based attacks,” involve manipulating the structure or content of a URL to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications. Attackers can use various techniques, such as encoding, injecting malicious code, or manipulating parameters, to deceive a system into performing unintended actions, accessing unauthorized data, or executing malicious scripts.
- File inclusion :- A file inclusion attack is a type of cyber attack that exploits vulnerabilities in a web application to execute malicious code by including files that are not intended to be accessed.
- Man in the middle attack :- If a third party manages to insert themselves between your device and the web site/application you’re connected to, you’ve just fallen victim to a “man in the middle” attack.
- System-based attacks :-
- Virus
- Worm
- Trojan
- Backdoor
- Bots A bot attack
- Virus :- It is a type of software program that spread throughout computer files without the knowledge of a user. The computer program that replicates by inserting copies of itself into the other computer.
- Worm :- It is a type of malware function is to spread to uninfected computer it originates from email attachments appear to be from trusted senders. It work same as virus.
- Trojan horse :- It is a malicious program that occurs unexpected changes to computer setting and unusual activity, even when the computer should be idle.
- Backdoor :- It is a method that bypasses the normal authentication process. A developer may create a backdoor so that an application or operating system can be accessed by troubleshooting or other purposes.
- Bots A bot (short for “robot”) :- It is an automated process that interacts with other network services. Some bot programs run automatically while other only execute commands when they received specific input.
c. Cyber security mechanism :-
- Cybersecurity controls are mechanisms used to prevent, detect and mitigate cyber threats and attacks. Mechanisms range from physical controls, such as security guards and surveillance cameras, to technical controls, including firewalls and multifactor authentication.
- Network Security is field in computer technology that deals with ensuring security of computer network infrastructure. As the network is very necessary for sharing of information whether it is at hardware level such as printer, scanner, or at software level. Therefore security mechanism can also be termed as is set of processes that deal with recovery from security attack. Various mechanisms are designed to recover from these specific attacks at various protocol layers.
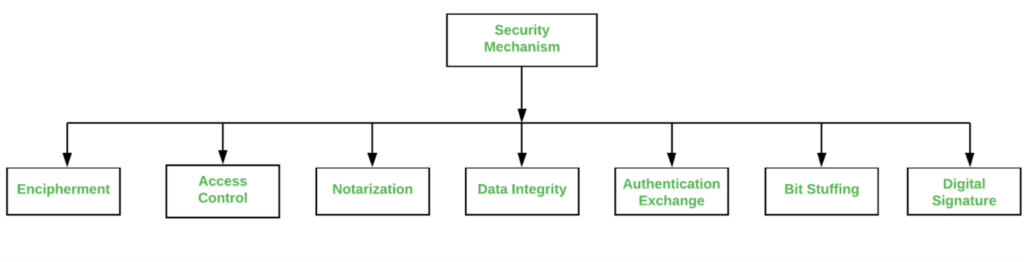
Types of Security Mechanism are
- Encipherment : This security mechanism deals with hiding and covering of data which helps data to become confidential. It is achieved by applying mathematical calculations or algorithms which reconstruct information into not readable form. It is achieved by two famous techniques named Cryptography and Encipherment. Level of data encryption is dependent on the algorithm used for encipherment.
- Access Control : This mechanism is used to stop unattended access to data which you are sending. It can be achieved by various techniques such as applying passwords, using firewall, or just by adding PIN to data.
- Notarization : This security mechanism involves use of trusted third party in communication. It acts as mediator between sender and receiver so that if any chance of conflict is reduced. This mediator keeps record of requests made by sender to receiver for later denied.
- Data Integrity : This security mechanism is used by appending value to data to which is created by data itself. It is similar to sending packet of information known to both sending and receiving parties and checked before and after data is received. When this packet or data which is appended is checked and is the same while sending and receiving data integrity is maintained.
- Authentication exchange : This security mechanism deals with identity to be known in communication. This is achieved at the TCP/IP layer where two-way handshaking mechanism is used to ensure data is sent or not.
- Bit stuffing : This security mechanism is used to add some extra bits into data which is being transmitted. It helps data to be checked at the receiving end and is achieved by Even parity or Odd Parity.
- Digital Signature : This security mechanism is achieved by adding digital data that is not visible to eyes. It is form of electronic signature which is added by sender which is checked by receiver electronically. This mechanism is used to preserve data which is not more confidential but sender’s identity is to be notified.
d. Different types of vehicle IoT application (spare parts where IoT application involve ) :-
- As the IoT is growing then new application will be introduced.
- Here the various type of application in vehicle IoT. The are
- Telematics: Gathering and transmitting data about vehicle location, speed, diagnostics, and driver behaviour for navigation, tracking, and insurance purposes.
- Infotainment Systems: Offering entertainment, connectivity, and communication services within the vehicle, including music, navigation, internet access, and smartphone integration.
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring vehicle health in real-time to predict potential issues or failures, enabling timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Fleet Management: Optimizing fleet operations by monitoring vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, route planning, and driver behaviour to improve efficiency and safety.
- Safety and Security: Implementing systems like collision detection, automatic emergency response, theft prevention, and remote vehicle disabling for enhanced safety and security.
- Autonomous Driving: Utilizing IoT for sensors, cameras, and AI algorithms to enable self-driving features and improve vehicle autonomy.
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring and controlling emissions, energy consumption, and other environmental factors to ensure compliance with regulations and promote sustainability.
e. IoT in different types of consumer application:-
What is consumer IoT (CIoT)?
CIoT, as the name suggests, is geared towards consumers. It involves smart devices and gadgets that individuals use in their homes or personal lives to enhance convenience, entertainment, health monitoring, and more.
- Consumer loT use cases encompass a wide range of consumer-oriented applications, such as smart home devices (thermostats, cameras, appliances), wearable fitness trackers, smart watches, connected cars, and smart entertainment systems. CloT focuses on improving daily life and providing users with personalized, connected experiences.
- These applications of CIoT may vary as per your requirement, and the services within can be customised according to what you need. And for offering you these services, you can trust the reputed custom enterprise software development company with IoT experts. So let us dive into the discussion of various CIoT application, and they are:
- Smart homes:

- A home where technology seamlessly integrates with daily life is what smart homes stand for. These connected spaces use loT devices to create efficient, convenient, and secure living environments. From thermostats that learn your preferred temperature settings to smart security systems that allow remote monitoring, smart homes redefine comfort and safety.
- By implementing smart home solutions, your business can offer customers a lifestyle upgrade, providing them control at their fingertips, ensuring energy efficiency, and enhancing their overall living experience.
- Smart healthcare:

- In the realm of healthcare, consumer loT is a game-changer. Smart healthcare solutions encompass wearable devices, remote monitoring systems, and loT-enabled medical equipment. Patients can monitor their vitals in real-time, and healthcare providers can access accurate data, leading to proactive, personalized care.
- Consumer loT application in healthcare not only improves patient outcomes but also streamlines operations for healthcare professionals. By integrating these technologies, your business can contribute to a healthier society while tapping into the growing healthcare technology market.
- Smart workplaces:

- Another application of CloT is to make workplaces smart by leveraging the power of loT technology to create productive, efficient, and employee-friendly environments. Smart office or workplace offers multiple perks such as lighting adjustments based on natural daylight, meeting rooms that anticipate your schedule, and desks that adapt to ergonomic preferences.
- loT-enabled collaboration tools foster seamless communication and boost productivity. Smart workplaces enhance work experience, improve employee well-being, and optimize office resources. By offering smart workplace solutions, your business can cater to the evolving needs of modern enterprises, enhancing efficiency and employee satisfaction.
- Smart entertainment:

- Consumer loT application is also applied to the entertainment sector; it has transformed the way we experience entertainment. Smart TVs offer personalized content recommendations, gaming consoles provide immersive experiences, and streaming services adapt to individual preferences.
- loT enables interactive, customized entertainment options, making leisure time more enjoyable. By incorporating loT into entertainment devices, your business can captivate customers with tailored experiences, ensuring they stay engaged and entertained.
- Smart wearables:

- Wearable devices have become indispensable companions in our daily lives. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and augmented reality glasses enhance our activities and interactions. Wearables track fitness goals, provide real-time notifications, and even offer health monitoring features.
- These devices seamlessly integrate into our routines, providing valuable insights and enhancing user experiences by gathering the required data. You can always leverage the cloud integration services to create the platform for saving these data and use them as per requirement.
- By developing innovative wearables, your business can tap into the growing market of health-conscious consumers, offering them products that blend fashion, functionality, and loT technology.
- Asset tracking:

- Consumer loT-based asset tracking is a boon if your business is dealing with logistics, manufacturing, or inventory management. Through sensors and GPS technology, assets can be tracked in real time.
- Whether it’s monitoring shipments, managing inventory, or ensuring the security of valuable equipment, asset-tracking solutions offer precision and efficiency. By providing your target audience with reliable asset tracking systems, your business can streamline operations, reduce losses, and enhance overall supply chain management.
f. Role of generative AI in cyber security :-
Generative AI In the context of cybersecurity plays a multifaceted role, revolutionizing traditional defence mechanisms and augmenting the capabilities of cybersecurity professionals. Let’s explore some key roles of Generative AI in cybersecurity:
- Generate realistic training data:
We can use generative AI to generate realistic training data for machine learning models to detect and prevent attacks. Generative AI can help to create this data by generating realistic examples of phishing emails, fake websites, and malicious code.
- Develop new security tools:
Security experts can develop new security tools using generative AI to detect and prevent attacks. Generative AI can be employed to create tools. These tools can generate realistic phishing emails and fake websites. These tools can be used to train machine learning models or to assist security analysts in identifying and investigating potential attacks.
- Improve the security of existing systems:
Traditional cybersecurity measures can sometimes suffer from latency issues, causing delays in identifying and responding to cyber threats. Generative AI’s real-time threat detection capabilities allow for rapid response times, reducing potential damages and minimizing the impact of cyber attacks.
- Proactive Defence:
Traditional cybersecurity often follows a reactive approach, responding to incidents after they occur. Generative AI empowers organizations to adopt a proactive stance, predicting & mitigating potential threats before they materialize.
- Generate attack simulations:
Security analysts can use generative AI to generate attack simulations to train themselves and test the effectiveness of security systems. They can use these simulations to create realistic scenarios to practice their skills. Security experts can use these tools to test security systems. By observing how security systems respond to different types of attacks, experts can assess their effectiveness.
- Automating Cybersecurity Tasks:
Cybersecurity professionals are burdened with numerous routine tasks, diverting their attention from more critical issues. Generative AI is capable of automating repetitive tasks like log analysis, threat hunting, and incident response. This frees up human experts to concentrate on strategic and complex challenges.
- Generate synthetic data:
Generative AI can be used to generate synthetic data that can be used to supplement real data. This can be useful for training machine learning models or for testing the effectiveness of security systems. Synthetic data can be generated that closely resembles real data. This synthetic data is devoid of any sensitive information.
- Automate security tasks:
Generative AI is a powerful tool that can automate security tasks. These tasks include generating reports, detecting anomalies, and responding to incidents. This can free up security analysts to focus on more important tasks and can help to improve the efficiency of security operations.
- Improve the security of the supply chain:
Generative AI identifies and mitigates risks to improve the security of the supply chain. You can use generative AI to generate realistic examples of attacks that could be launched against the supply chain. These examples can be used to test the security of the supply chain. The vulnerabilities identified through these tests can then be addressed.
- Increase the resilience of organizations:
Generative AI can be used to increase the resilience of organizations by helping them to recover from attacks. This can be done by using generative AI to generate realistic examples of attacks that could be launched against an organization. These examples can then be used to develop plans for how to recover from attacks.
Application of generative AI in cyber security:
- There are a number of potential applications, including:
- Creating realistic phishing emails: Cybercriminals use generative AI to create realistic phishing emails that trick users into clicking on malicious links or providing sensitive information.
- Generating fake websites: Malicious actors can use generative AI to create fake websites that appear to be legitimate. This can deceive users into disclosing their personal information or downloading harmful files.
- Generating malicious code: Malicious actors can use generative AI to generate code that exploits vulnerabilities in computer systems.
g. how generative AI helpful to reduce risk of cyber harm :-
- Generative AI can play a role in reducing cyber harms in several ways. They are:
- Enhancing security measures: Generative AI can help in creating more robust security measures by predicting potential vulnerabilities in systems. It can simulate attacks to identify weaknesses, allowing for proactive strengthening of defences.
- Developing defence mechanism: AI-generated models can aid in creating more advanced intrusion detection systems. These systems can recognize patterns of malicious behaviour, identifying threats in real-time and enabling quicker responses to cyber attacks.
- Creating realistic training data: Generative AI can produce synthetic data that closely mimics real data. This is invaluable for training machine learning models used in cybersecurity without risking exposure to sensitive or confidential information.
- Automating threat detection: AI algorithms can continuously monitor networks and systems, detecting anomalies or suspicious activities faster than traditional methods. Generative models can aid in creating more sophisticated algorithms for this purpose.
- Predicting and preventing attacks: By analysing historical data, generative AI can predict potential cyber threats and pre-emptively suggest measures to prevent attacks, thereby reducing the overall risk of cyber harms.

